Overview
Approved by the FDA in 1996, this medication is used in the second-line treatment for hypertension. Trandolapril, an ACE inhibitor (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor), and Verapamil, a calcium-channel blocker, are combined in this medication. The medications' complementary modes of action lower blood pressure and reduce peripheral resistance. Oral Verapamil and Trandolapril work more effectively together than administering either drug alone to lower blood pressure and treat proteinuria. It contains extended-release Verapamil and Trandolapril with immediate release. It is administered once daily and might be practical for those patients who take both medications separately.
How Do the Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets Work?
This medication helps manage hypertension by reducing the load on the heart by relaxing the blood vessels. This medication also enables smooth blood flow in the blood vessels by decreasing the production of certain chemicals which are responsible for the tightening of the blood vessels. Being an extended-release (ER) tablet, it disintegrates slowly over time, thereby increasing the drug's efficacy.
Uses of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets:
It is used in the management or second line treatment of hypertension. This medication cannot cure hypertension but can only help manage it.
Dosage and Administration:
Available in the form of tablets and administered orally, one pill of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER should be taken once daily with food. The dosing can vary with the combination of 1 to 4 mg of Trandolapril and 180 to 240 mg of Verapamil.
-
Missed Dose: In cases of missed doses, patients should take their dose as soon as they remember. Nevertheless, if it is almost time for the next dose, the patients can skip the missed dose and administer the consequent dose. Patients should avoid taking two doses together to compensate for the missed dose.
Use in Specific Populations:
1. Allergies -
Patients should inform the physician if they have ever had any unusual or allergic reaction to this drug or any other drugs. They should also inform the health care professional if they have a history of allergies associated with foods, dyes, preservatives, or animals.
2. Pediatric -
Since legitimate studies have not been performed in the pediatric population, this medication should be avoided in this group.
3. Breastfeeding -
Due to the lack of adequate studies in this population, it is advisable that lactating women determine infant risk when using this medication during breastfeeding.
4. Hepatic Impairment -
The metabolism of Trandolapril is altered in patients with hepatic impairment. Hence, following the oral administration of this drug in patients with mild to moderate alcoholic cirrhosis and other forms of liver disease, the plasma concentrations of Trandolapril and Trandolaprilat are greater by nine-fold and two-fold, respectively, when compared with their normal counterparts. Hence, doctors should consider this before prescribing this drug to patients diagnosed with liver disease.
5. Renal Impairment -
The metabolism of Trandolapril is impaired in patients with renal impairment and in patients receiving hemodialysis. Compared to the normal counterparts, the plasma concentrations of Trandolapril and its metabolite -Trandolaprilat, are approximately greater by two-fold. Additionally, renal clearance also reduces by 85 % in such patients. Due to the decreased clearance, doctors should constantly monitor such patients if they are prescribed this drug.
6. Pregnancy -
ACE- inhibitors can harm the developing fetus and even cause death when administered during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Hence, doctors should not prescribe this drug to pregnant women, and when pregnancy is suspected, this drug should be discontinued immediately.
Drug Interactions:
Certain medications cannot be used together to avoid interactions; however, in some cases, sometimes these medications are prescribed by changing the dose and or taking the necessary precautions required. Using Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets with any of the following medicines are not recommended:
-
Aliskiren.
-
Dofetilide.
-
Flibanserin.
-
Dofetilide.
-
Lomitapide.
-
Sacubitril.
-
Eliglustat.
-
Colchicine.
The use of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets with any of the following medicines is usually not recommended. If the physician chooses to prescribe Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets, then a dose modification is done in the following medications:
-
Abametapir.
-
Acalabrutinib.
-
Adenosine.
-
Afatinib.
-
Alfentanil.
-
Alprazolam.
-
Amiloride.
-
Amiodarone.
-
Aprepitant.
-
Atazanavir.
-
Atenolol.
-
Atorvastatin.
-
Avapritinib.
-
Azathioprine.
-
Azilsartan.
-
Azilsartan medoxomil.
-
Benzhydrocodone.
-
Berotralstat.
-
Betaxolol.
-
Betrixaban.
-
Bevantolol.
-
Bisoprolol.
-
Bosutinib.
-
Brexpiprazole.
-
Brigatinib.
-
Bucindolol.
-
Bupivacaine.
-
Bupivacaine liposome.
-
Buprenorphine.
-
Candesartan.
-
Canrenoate.
-
Carbamazepine.
-
Carteolol.
-
Carvedilol.
-
Celiprolol.
-
Ceritinib.
-
Cilostazol.
-
Clarithromycin.
-
Clonidine.
-
Clopidogrel.
-
Clozapine.
-
Cobimetinib.
-
Codeine.
-
Conivaptan.
-
Cyclobenzaprine.
-
Dabigatran etexilate.
-
Dantrolene.
-
Daridorexant.
-
Deflazacort.
-
Digoxin.
-
Dihydrocodeine.
-
Dilevalol.
-
Domperidone.
-
Doxorubicin.
-
Doxorubicin hydrochloride liposome.
-
Dronedarone.
-
Edoxaban.
-
Elexacaftor.
-
Encorafenib.
-
Entrectinib.
-
Epirubicin.
-
Eplerenone.
-
Eprosartan.
-
Erythromycin.
-
Esmolol.
-
Everolimus.
-
Fedratinib.
-
Fentanyl.
-
Fosaprepitant.
-
Fosnetupitant.
-
Hydrocodone.
-
Ibrutinib.
-
Ifosfamide.
-
Infigratinib.
-
Irbesartan.
-
Ivabradine.
-
Ivacaftor.
-
Ivosidenib.
-
Ketoconazole.
-
Labetalol.
-
Lacosamide.
-
Lefamulin.
-
Lemborexant.
-
Levobunolol.
-
Lithium.
-
Losartan.
-
Lovastatin.
-
Lumateperone.
-
Lurasidone.
-
Lurbinectedin.
-
Mavacamten.
-
Meperidine.
-
Mepindolol.
-
Mepivacaine.
-
Metipranolol.
-
Metoprolol.
-
Mitapivat.
-
Mobocertinib.
-
Morphine.
-
Morphine sulfate liposome.
-
Nadolol.
-
Naloxegol.
-
Nebivolol.
-
Neratinib.
-
Netupitant.
-
Nilotinib.
-
Olaparib.
-
Olmesartan.
-
Palbociclib.
-
Pemigatinib.
-
Penbutolol.
-
Pentazocine.
-
Pexidartinib.
-
Pindolol.
-
Piperaquine.
-
Pixantrone.
-
Potassium phosphate.
-
Propranolol.
-
Ranolazine.
-
Relugolix.
-
Rimegepant.
-
Selpercatinib.
-
Selumetinib.
-
Simeprevir.
-
Simvastatin.
-
Siponimod.
-
Sirolimus.
-
Sirolimus protein-bound.
-
Sotalol.
-
Spironolactone.
-
Sufentanil.
-
Tacrolimus.
-
Talazoparib.
-
Talinolol.
-
Tertatolol.
-
Tezacaftor.
-
Tolvaptan.
-
Topotecan.
-
Tramadol.
-
Triamterene.
-
Trimethoprim.
-
Ubrogepant.
-
Valsartan.
-
Venetoclax.
-
Venlafaxine.
-
Voclosporin.
Other Interactions:
The use of alcohol and tobacco with Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets can result in certain unwanted interactions. Hence, the healthcare professional must be informed about medications, alcohol, or tobacco.
Food Interactions:
Patients on Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets should avoid grapefruit.
For Patients
What Is Hypertension?
Commonly known as increased blood pressure, hypertension is a medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels. Blood pressure refers to the pressure of the blood that pushes against the walls of the blood vessels which carry oxygen-rich blood. Although the blood pressure drops and rises throughout the day and varies for every individual, a normal blood pressure value is considered at 120/80 mmHg. When the pressure is elevated, the heart experiences additional load and tends to work harder to pump blood against a high-pressure gradient. People can be hypertensive yet asymptomatic for years. Hypertension is not associated with a specific set of symptoms, but occasionally, hypertensive patients can experience the following symptoms -
-
Nose bleeds.
-
Headaches.
-
Chest pain.
-
Breathlessness.
What Are the Causes of Hypertension?
The exact cause of hypertension may not be clear, but the following factors make a person susceptible to hypertension -
-
Excess salt intake.
-
A diet rich in fats and processed foods.
-
Alcohol and caffeine abuse.
-
Disturbed or diminished sleep.
-
Family history of blood pressure.,
-
Lack of physical activity or exercise.
-
Increased blood sugar.
What Are the Consequences of Untreated Hypertension?
When elevated blood pressure levels are not returned to the normal range, the quality of life can be greatly impaired. The following complications can precipitate -
-
Heart attack.
-
Kidney damage.
-
Eye problems, such as blurry vision or vision loss.
-
Aneurysm (a bulge or widened portion on the walls of the blood vessels).
-
Mental disorientation.
What Are Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets, and How Do They Work?
These tablets are a combination of two classes of drugs used to control hypertension. Trandolapril belongs to the class of ACE inhibitors (also known as an angiotensin-converting enzyme), whereas Verapamil hydrochloride belongs to the class of calcium channel blockers.
They are a form of extended-release tablet, meaning that the drug is released slowly over a set period, improving the drug's efficacy.
This medication helps manage hypertension by reducing the load on the heart by relaxing the blood vessels. This medication also enables smooth blood flow in the blood vessels by decreasing the production of certain chemicals which are responsible for the tightening of the blood vessels.
How Should Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets Be Used?
-
This medication is dispensed in the form of tablets and is administered orally, one tablet per day.
-
The dosing can vary with the combination of 1 to 4 mg of Trandolapril and 180 to 240 mg of Verapamil.
-
The tablets should be swallowed whole, and patients should avoid breaking, crushing, and chewing these tablets.
-
Patients should consult a physician before modifying the dose and frequency of administration of this drug.
Missed Dose: In cases of missed doses, patients should take their dose as soon as they remember. Nevertheless, if it is almost time for the next dose, the patients can skip the missed dose and administer the consequent dose. Patients should avoid taking two doses together in order to compensate for the missed dose.
What Special Dietary Instructions Must Be Followed?
This medication tends to upset the stomach. Hence it should always be taken with food or milk. Doctors may advise a low-salt diet. Patients should consult their doctors before using salt substitutes containing potassium.
What Are the Side Effects of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets?
Following a dose of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets, the following side effects can be experienced by people -
-
Lightheadedness or dizziness.
-
Sore throat.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Hoarseness of voice.
-
Slow heartbeats.
-
Upset stomach.
-
Fatigue.
-
Flushing.
-
Cough.
If any of the following side effects are experienced, people should rush to the hospital -
-
Shortness of breath.
-
Difficulty in swallowing.
-
Skin rash.
-
Yellowing of the eyes and skin.
-
Unexplained fever.
-
Swelling of the eyes, lips, tongue, face, arms, and legs.
-
Loss of consciousness.
How Are Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets Stored and Discarded?
This medication should be stored in its original packaging at temperatures 15 to 25 degrees Celsius (59 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit). Measures should be taken to ensure protection from sunlight and air contamination. This medication should not be flushed down the drain or toilet. Rather the disposal of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets should be under local guidelines and medical regulatory bodies. Measures should be taken to ensure that children, other people, and pets do not consume them while disposing of this medication. If not expired, unneeded medicines can also be returned to the pharmacist.
Who Should Not Use Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets?
This medication should not be used under the following conditions -
-
Pregnancy.
-
Pediatric population.
-
First-line therapy of hypertension.
-
It should be avoided in people allergic to this drug, its components, or ACE inhibitors.
-
Patients with severe ventricular dysfunction.
-
Hypotension.
-
Patients with a second or third atrioventricular block (unless patients have a functioning artificial ventricular pacemaker).
-
Sick sinus syndrome (unless patients have a functioning artificial ventricular pacemaker).
-
Patients with atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation along an accessory bypass tract (for example, Lown-Gananong-Levine syndrome).
What Should Be Informed to the Healthcare Professional Before Using Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets?
Before taking this medication, patients should inform their physicians of the following -
-
Previous history of allergies to the following medications -
-
Trandolapril.
-
Verapamil.
-
Benazepril.
-
Captopril.
-
Enalapril.
-
Fosinopril.
-
Lisinopril.
-
Moexipril.
-
Quinapril.
-
Ramipril or any other drugs.
-
Physicians should inform about increased blood sugar levels or any previous history of diabetes. They should also be informed if patients are taking the drug Aliskiren. Normally, Trandolapril and Verapamil Hcl is not prescribed in patients diagnosed with diabetes and also when patients are on Aliskiren therapy.
-
Physicians and pharmacists should be informed about the prescription and nonprescription medications that the patients are taking. Special emphasis should be given to the following drugs and supplements -
-
Albuterol.
-
Ventolin.
-
Allopurinol.
-
Antacids.
-
Betamethasone.
-
Carbamazepine.
-
Chemotherapy medications.
-
Cimetidine.
-
Cortisone.
-
Cyclosporine.
-
Dantrolene.
-
Dexamethasone.
-
Diuretics or water pills.
-
Fentanyl.
-
Fludrocortisone.
-
Heart and blood pressure medications such as beta-adrenergic blockers, Digoxin, Disopyramide, Flecainide, Procainamide, and Quinidine
-
Hydrocortisone.
-
Lithium.
-
Medications that suppress the immune system.
-
Medications to treat depression or psychiatric conditions.
-
Medications to treat glaucoma.Medications to treat pain.
-
Muscle relaxants.
-
Methylprednisolone.
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
-
Medications for high blood pressure or diabetes.
-
Phenobarbital.
-
Phenytoin.
-
Potassium supplements.
-
Prednisolone.
-
Prednisone.
-
Rifampin.
-
Theophylline.
-
Triamcinolone.
-
Vitamins or herbal products.
-
Physicians should be informed if the patients have or have a history of liver, heart, or kidney disease.
-
Physicians should also be informed about the following conditions -
-
A recent heart attack.
-
Irregular heartbeat.
-
Muscular dystrophy.
-
Gastrointestinal obstruction (strictures).
-
Diabetes.
For Doctors
Indications of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets:
This medication cannot cure hypertension but can only help manage it. It is used in the second-line treatment of hypertension.
Contraindications of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets:
This medication is contraindicated in the following conditions -
-
First-line therapy of hypertension.
-
It should be avoided in people allergic to this drug, its components, or ACE inhibitors.
-
Patients with severe ventricular dysfunction.
-
Hypotension.
-
Cardiogenic shock.
-
Patients with a second or third atrioventricular block (unless patients have a functioning artificial ventricular pacemaker).
-
Sick sinus syndrome (unless patients have a functioning artificial ventricular pacemaker).
-
Patients with atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation along an accessory bypass tract (for example, Lown-Gananong-Levine syndrome).
-
Pregnant women.
-
Pediatric population.
Pharmacology:
Mechanism of Action Of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets:
This medication is a fixed combination drug made of a calcium channel blocker with a slow-release form (Verapamil hydrochloride) and an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, an instant-release form (Trandolapril). Trandolapril competitively inhibits angiotensin-converting enzymes, which lowers plasma angiotensin II concentrations. As a result, vasoconstriction, renin activity, and aldosterone production are reduced, which aids in lowering blood pressure. Additionally, Verapamil, a non-dihydropyridine calcium-channel blocker, prevents extracellular calcium ions from entering myocardial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells through their membranes without altering serum calcium concentrations. This helps prevent cardiac and vascular smooth muscle contraction, which dilates the main coronary and systemic arteries.
Dosage and Administration:
Available in the form of tablets and administered orally, one pill of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER should be taken once daily with food. The dosing can vary with the combination of 1 to 4 mg of Trandolapril and 180 to 240 mg of Verapamil.
-
Missed Dose: In cases of missed doses, patients should take their dose as soon as they remember. Nevertheless, if it is almost time for the next dose, the patients can skip the missed dose and administer the consequent dose. Patients should avoid taking two doses together in order to compensate for the missed dose.
Adverse Effects Of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets:
Following a dose of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER tablets, the following side effects can be experienced by people -
-
Lightheadedness or dizziness.
-
Sore throat.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Heartburn.
-
Hoarseness of voice.
-
Slow heartbeats.
-
Upset stomach.
-
Fatigue.
-
Flushing.
-
Cough.
If any of the following side effects are experienced, patients should rush to the hospital -
-
Anaphylaxis.
-
Yellowing of the eyes and skin.
-
Unexplained fever.
-
Loss of consciousness.
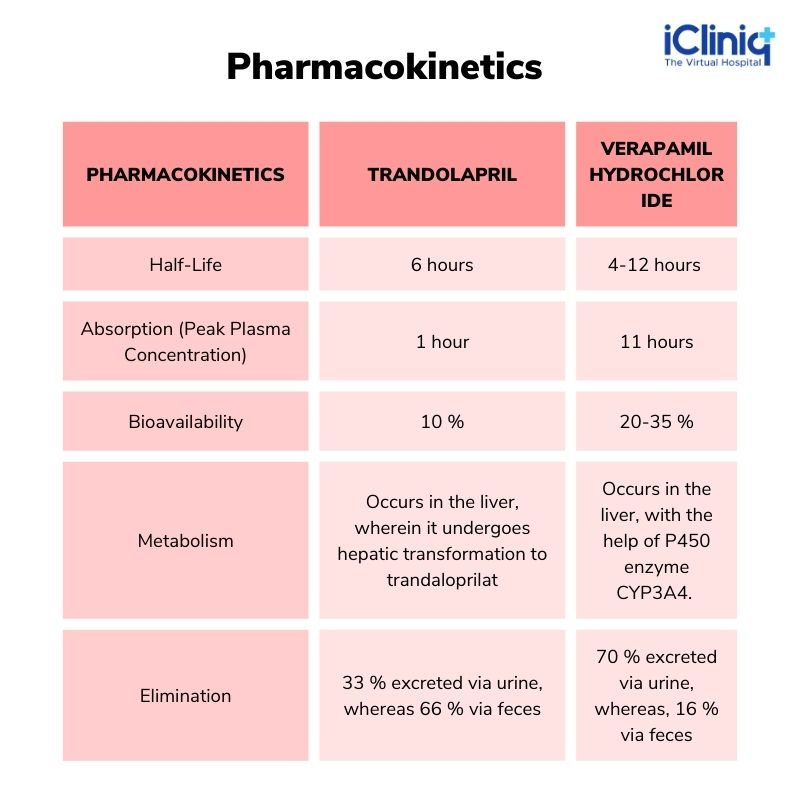
Pharmacokinetics Of Trandolapril and Verapamil HCL ER Tablets: