Drug Overview
Valethamate, also known as Valethamate bromide belongs to the anticholinergic or antispasmodics group of drugs and is used widely by the obstetrician for dilation of cervix during delivery. Valethamate bromide is used for the management of pain and spasm in the first stage of labor. The drug Valethamate bromide is yet not approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) as it does not satisfy all the guidelines recommended by WHO (world health organization). The safety and effectiveness of the use of the drug Valethamate bromide are yet not established and are still under research. The article further sheds light on the mechanism of action, pharmacological considerations, and effectiveness of the drug Valethamate in specific populations.
How Does the Drug Valethamate Bromide Work?
The drug Valethamate bromide is an antispasmodic agent that works by dilating the smooth muscles of the intestine and cervix, thus reducing the spasms. Valethamate bromide inhibits the acetylcholine receptors (causes muscle constriction) and reduces pain and spasm during labor, menstruation, bladder stones, and kidney stones.
Uses:
Valethamate bromide is used in reducing pain and spasm due to the following:
-
Bladder stones.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Menstruation.
-
During labor while delivery (helps dilate the cervix during delivery).
Doses:
The drug is available in both oral tablets and injection forms. The doses are:
-
Oral Form: In the dose of 10 and 20 milligrams.
-
Injection Form: Injection Solution is available in the dose of 4 mg and 8 mg vials.
Warnings:
-
Risk of Blurred Vision: The drug Valethamate bromide increases the risk of increased pressure within the eyes and paralysis of ciliary muscles, so it should be avoided or used cautiously in patients with eye problems.
-
Risk of Thyrotoxicosis: The drug Valethamate bromide increases the risk of thyrotoxicosis (increase in the thyroid hormones), so it should be used cautiously in patients with thyroid disorders.
For Patients
Why Is the Drug Valethamate Used During the Delivery?
Despite very little information known about Valenthamate, it is used in pregnant women during the first stage of labor for cervical ripening and dilation to reduce the time spent in labor for monitoring women. The drug fastens the process in crowded delivery rooms and reduces labor time in pregnant women.
What Are the Effects of Prolonged Labor on Pregnant Women?
There are various effects of prolonged labor in pregnant women, as per documented research such as.
-
Maternal burnout (feeling of fatigue or exhaustion in the mother during labor).
-
Postpartum bleeding (excessive bleeding after childbirth).
-
Sepsis (life-threatening complication due to infection).
-
Fetal distress (seen during prolonged labor and characterized by decreased oxygen supply to the fetus during labor or pregnancy).
-
Fetal asphyxia (lack of blood circulation and gaseous exchange in the babies’ brains during or after birth).
Know More About Valethamate Medication
When and Why to Take Valethamate?
Valethamate bromide can be taken at the exact dose and scheduled as the doctor prescribes. It is usually prescribed by the doctor in pregnant females for dilation of the cervix during delivery and for reduction of abdominal pain and spasm.
Things to Inform The Doctor Before They Prescribe Valethamate Medication:
-
In case of any allergies to any drug or its composition.
-
In case of any underlying systemic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, liver damage, and kidney disease.
-
Inform the doctor in case of any medicines (prescribed or non-prescribed) ongoing for any medical condition.
-
Inform the doctor if undergone any surgeries in the past.
Starting Valethamate Medication:
How To Take Valethamate?
-
Valethamate bromide tablets can be taken as a whole with water with or without food in the exact dose and schedule as prescribed by the doctor.
-
It is advised not to chew, crush, or break the tablet.
-
Avoid abruptly stopping the drug in case of relief of symptoms.
Things to Do After One Starts Taking Valethamate:
-
Inform the doctor in case of any allergic reactions develop after starting Valethamate medication.
-
In case of any adverse reaction seen, like blurring of vision, dry mouth, rashes, etc., after taking the drug, it should be informed to the doctor.
-
In case of improvement in the symptoms after starting the drug, it should be updated to the doctor during follow-up sessions.
Look Out for the Side Effects:
Common Side Effects:
-
Fever.
-
Rashes.
-
Headaches.
-
Nausea.
-
Vomiting.
-
Dry mouth.
-
Flushing.
-
Dryness of skin.
-
Increased thirst.
-
Reduction of bronchial secretions.
-
Palpitations.
Serious Side Effects:
-
Tachycardia.
-
Blurred vision.
-
Difficulty in swallowing.
-
Urinary retention.
-
Difficulty in talking.
-
Dilatation of pupil.
-
Cycloplegia (paralysis of ciliary muscles of the eye).
Dietary Alterations:
No information is available for any kind of food interaction with Valethamate. Alcohol consumption should be avoided when under Valethamate bromide as it can cause severe adverse reactions if the drug interacts with alcohol.
What Should Be Done if the Dose Is Missed?
If the dose of the drug is missed, it is recommended to take when remembered. Skip the missed dose if it's time for the next dose and take the scheduled dose. Do not overdose to compensate for the missed dose.
What Should Be Done in Case of Overdose?
-
Drug overdose can be managed by symptomatic and supportive measures.
-
Antispasmodic or anticholinergic effects of Valethamate bromide can be reversed by giving the drug Physostigmine in the dose of 1 mg or 3 mg intramuscularly (IM). The dose can be repeated if needed.
Avoid Self-Prescription:
The drug Valethamate is unavailable over the counter. The drug Valethamate bromide is prescribed by the healthcare professionals only if clinically indicated. The drug Valethamate bromide is prescribed by the healthcare professionals only if clinically indicated.
Staying On Valethamate:
-
Inform the doctor if any side effects are observed.
-
Inform the doctor in case of worsening of the symptoms after consuming the drug.
-
Take the dose as suggested by the doctor.
For Doctors:
Indications:
Valethamate is indicated in the conditions like:
-
For cervix dilation during delivery to reduce the labor time.
-
To manage the muscle spasm during constipation or pain due to a bloated stomach.
-
Management of muscle spasms during dysmenorrhoea (cramps during menstruation). It helps in reducing abdominal cramps.
-
During tenesmus (urge to defecate).
-
Relieves pain and spasm from urinary colic (kidney stones).
-
Relieves pain and muscle spasms from biliary colic (bladder stones)
Pharmacology:
Mechanism of Action:
Valethamate bromide is an antispasmodic or anticholinergic group of drugs. It acts against acetylcholine receptors (causes muscle constriction) and results in dilatation of the smooth muscles of the intestine and uterine, thus helping in the reduction of muscle spasms. Both peripheral and central neuronal action is shown by the drug Valethamate Bromide.
Pharmacodynamics
The drug Valethamate bromide is a smooth muscle relaxant. The drug Valethamate bromide shows competitive inhibition with acetylcholine receptors. Valethamate inhibits the muscarinic receptors and thus causes the relaxation of smooth muscles.
Chemical Taxonomy:
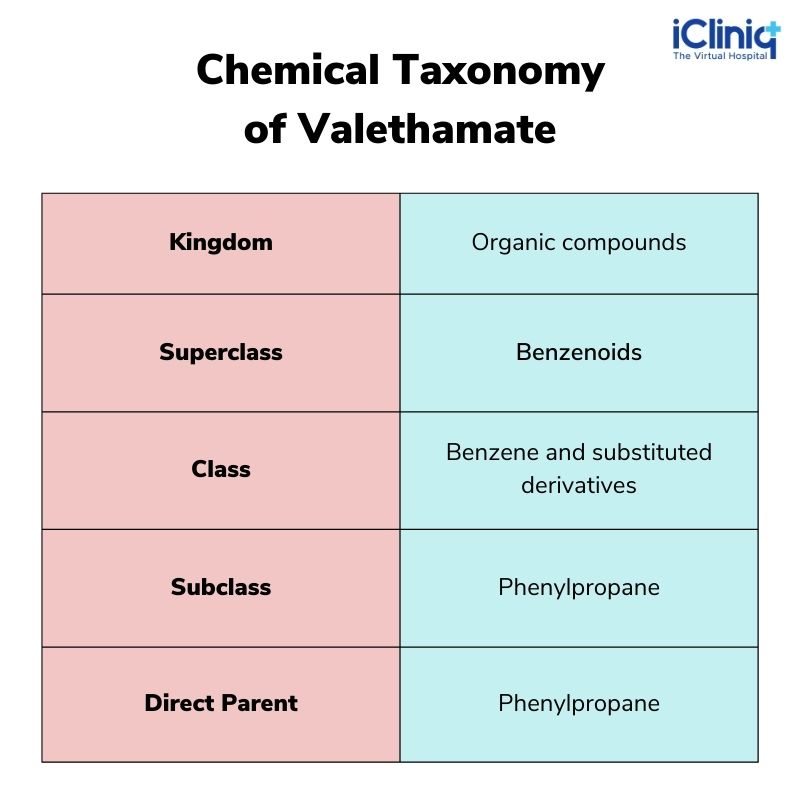
Ingredients:
One mL of Valethamate bromide contains:
Active Ingredients:
-
Valethamate Bromide - 8 mg.
Inactive Ingredients
-
Sodium Chloride - 8 mg.
-
Distilled water for dilution.
Pharmacokinetics:
Onset of Action:
The drug Valethamate bromide starts acting within 20 to 30 minutes after administration.
Absorption:
The drug Valethamate is absorbed well after parenteral administration (intravenous or intramuscular injections).
Elimination:
The drug Valethamate bromide and its metabolites are excreted through urine.
Metabolism:
The drug is metabolized completely in the liver.
Distribution:
The drug Valethamate is widely distributed in the body. It can cross the placenta, and traces are present in the breast milk.
Toxicity:
In case of toxicity, inform the poison control center quickly. The toxicity of the drug can affect the eyes, liver, and kidneys.
Half-Life:
The average half-life of the drug Valethamate bromide is around four hours.
Habit Forming:
No habit-forming tendency has been reported yet from Valethamate bromide.
Specific Properties of Valethamate Bromide:
-
Appearance: Valthemate bromide appears whitish powder to whitish crystals in appearance.
-
Physical State: Solid.
-
Melting Point: The melting point of Valethamate bromide is 127 degree Celsius.
-
Purity: High-performance liquid chromatography test reveals a purity of around 98 percent.
-
Water Solubility: It is completely soluble in water.
Storage:
-
The drug Valethamate bromide can be stored at normal room temperature.
-
It should be stored away from light and out of reach of children.
-
The drug with expired dates or discolored solutions should be discarded.
-
The drug should not be refrigerated.
Doses and Forms:
The drug Valethamate bromide is available in both oral tablets and injection forms. The dosage of the drug available are:
Adult Dose:
-
Oral Tablet: Oral tablet is available in the dosage of 10 milligrams and 20 milligrams. It is prescribed by the doctor once a day for the management of underlying smooth muscle spasms.
-
Parental Form: The drug Valethamate bromide is administered by healthcare professionals at the dose of 4 mg or 8 mg intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM) to manage muscle spasms.
Pediatric Dose:
The drug is not indicated in children and neonates.
Administration of the Drug:
-
The drug is administered by the healthcare professional into the veins (IV) or into the muscles (IM) for the dilation of the cervix during delivery. It can also be prescribed in oral tablet form to the patients once daily to reduce muscle spasms.
-
The drug should not be stopped abruptly. The drug dose is gradually stopped by the doctor.
Contraindications:
The drug Valethamate bromide is contraindicated in the following conditions:
-
In people with allergy or hypersensitivity reactions to Valethamate bromide.
-
In the case of enlarged prostate.
-
In the case of pyloric stenosis (constriction of pyloric muscles of the stomach seen mostly in babies).
-
Paralytic ileus (failure of bowel movements resulting in intestinal obstruction causing restriction in food movement).
-
In patients with ulcerative colitis (long-term inflammatory bowel disease).
-
Severe colon infection (toxic megacolon).
-
People with closed-angle glaucoma (sudden increase in pressure within the eyes).
-
In patients with myasthenia gravis (weakness of the skeletal muscles).
Drug Interactions:
-
The drug Valethamate bromide may interact with other antispasmodic drugs.
-
The drug, if given along with antihistamines, phenothiazines, Disopyramide, and Quinidine, can potentiate the effects of the drug Valethamate. It delays other drug absorption and obstructs gastric emptying.
Other Specifications:
Valethamate in Pregnant and Lactating Women: The drug Valethamate bromide can be used in pregnant and lactating women only if recommended by the doctor for clinical purposes. However, the associated potential risks and benefits should be informed to the patient before administering the drug as the drug crosses the placenta and is produced in breast milk.
Valethamate While Driving: The drug Valethamate bromide can result in dilation of the pupil or blurring of vision. So, it is recommended to avoid driving and operating any heavy machinery when under Valethamate bromide
Valethamate in Patients with Liver Disease: Valethamate bromide should be used very carefully in patients with underlying liver diseases. Drug-dose adjustment is usually done by the healthcare provider in patients with liver disease.
Valethamate in Patients with Kidney Disease: Valethamate bromide safety is not determined in patients with kidney disorders, so it should be used cautiously. Drug-dose adjustments are usually required in patients with kidney disease.
Valethamate in Pediatric Patients: Valethamate bromide's safety and efficacy are yet not proven in pediatric patients. It can be used by the doctor only if clinically needed. The drug Valethamate is strictly contraindicated in neonates (newborns).
Valethamate in Geriatric Patients: The use of Valethamate bromide in elderly people can be done with caution. Complete systemic examination to rule out any underlying systemic disease is recommended before starting the drug Valethamate in old-age patients.











