Overview
Brincidofovir is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2021, under the FDA Animal Rule for the treatment of human smallpox disease. The drug's effectiveness was established against smallpox in vitro studies based on related variola, and orthopoxviruses. Also, the efficacy of the drug was obtained through the study of animal models infected with either orthopoxviruses or variola. In addition, the safety of the drug was established by evaluating non-smallpox indications, especially in people who received bone marrow transplants.
Brincidofivir is a lipid conjugate pro-drug that improves the delivery of drugs to the target cells and also reduces the nephrotoxicity caused by Cidofovir therapy. In addition, the drug also has greater bioavailability because of the formulation as a pro-drug; therefore, it makes it more suitable for oral administration than intravenous.
What Are the Indications of the Drug?
Brincidofovir is indicated for the treatment of variola virus disease, called human smallpox in adults, pediatrics, and neonates.
What Are the Contraindications of the Drug?
-
The drug is not recommended for treating any other medical condition or disease except human smallpox.
-
The effectiveness of the drug is only studied and evaluated in animal studies, and there are no human studies on smallpox-infected individuals.
-
The safety of the drug is studied in humans and young children of three months or above.
-
The drug should not be prescribed to an immunocompromised person, as it may not work effectively.
Dose and Administration
Tablets: The drug can be taken orally on an empty stomach or with approximately 400 calories, and 40 percent calories from fats (low-fat meals). The tablet is to be swollen completely without crushing or dividing.
Oral Suspension: The oral suspension of Brincidofovir can be taken on an empty stomach. It should be shaken well, and a proper dose dispenser syringe should be used while taking the drug dosage.
For patients who cannot swallow the drug directly, a nasogastric or gastrostomy tube or enteral tube can be used for drug administration in the following way:
-
Calibrated catheter-tip syringe is used to draw out the prescribed drug dose and then administered via an enteral tube.
-
The syringe is then filled with water up to 3 mL (milliliters) to administer the content through the enteral tube.
-
The catheter-tip syringe should be washed before and after the administration of the drug via the enteral route.
Recommended Dosage
The Drug Dosage of Brincidofovir Recommended For Pediatric and Adults Patients
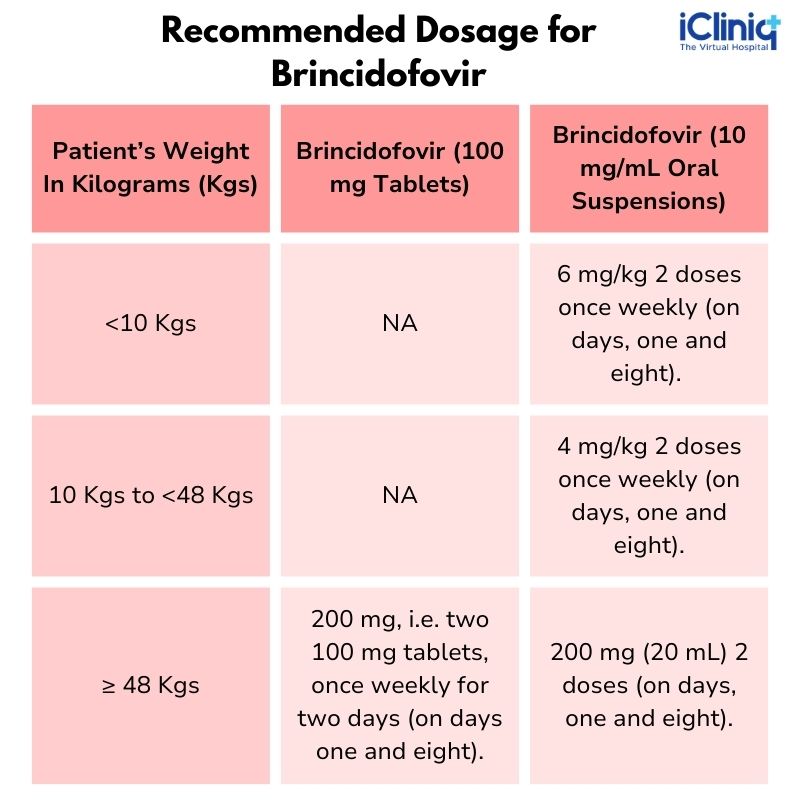
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Based on animal reproduction studies, the drug is unsafe to use in pregnant individuals, as it can cause harm to the fetus. However, there are no significant studies to show any drug-associated major birth defects, such as miscarriages, caused by Brincidofovir in pregnancy. In pregnant rats, during an animal reproduction study, an oral administration of Brincidofovir caused structural malformations and embryotoxicity during organogenesis. All these effects were seen with dosage exposure less than that of expected drug exposure for humans of Brincidofovir.
Lactation
No specific data is showing the presence of the drug in human milk, its effects on milk production, and infants. However, breastfeeding is not recommended in patients having smallpox because the variola virus has the potential to get transmitted through breast milk through direct contact with the breastfed baby.
Pediatric Use
The effectiveness and efficacy of the drug in pediatric patients are similar to that of adult patients and are completely based on animal model studies for orthopoxvirus diseases.
Geriatric Use
The severity and nature of the adverse effects of the drug are quite similar for young and older patients according to studies. Therefore, no dose alterations are required for patients 65 years and above.
Renal Impairment
No dose alterations are recommended for patients suffering from mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment, or end-stage renal diseases, and on dialysis.
Hepatic Impairment
It is clinically important to conduct a hepatic lab examination before prescribing Brincidofovir to a patient. However, no dose adjustment is required for a patient with hepatic impairment at any stage.
For Patients:
Why Is Brincidofovir Prescribed to a Person?
Brincidofovir is a prescription drug prescribed to treat smallpox in infants, children, and adults.
How Should the Drug Be Used?
-
The drug should be taken as prescribed by the doctor, in the recommended dosage only, that is 2 doses once a week (on days, one and eight).
-
A person should try not to skip or miss the dose of Brincidofovir.
-
The above-mentioned dosage and administration, and dietary recommendations should be strictly followed by the person while taking the drug dosage.
What Are the Side Effects of the Drug?
Liver Problems:
-
Discomfort in the stomach on the upper right side.
-
Dark urine.
Diarrhea:
It is a common side effect in people who are prescribed Brincidofovir, but the condition can become serious as well. The doctor should be immediately informed if a person has diarrhea with four or more stools in a day, unlike other usual days.
Other Common Side Effects:
-
Nausea.
-
Stomach Pain.
Less Common Side Effects:
-
Decreased appetite.
-
Peripheral edema.
-
Muscular weakness.
-
Dysgeusia (taste disorder).
-
Rash.
Overdose:
There is no clinical experience related to drug overdose from Brincidofovir. In case of any such event, monitor the person for any adverse effects and provide supportive care by contacting the nearest healthcare facility.
Missed Dose:
The drug dose should not be missed or skipped. Therefore, in case this happens consult the doctor for proper assistance, Do not take a missed dose without proper knowledge if it is already time for the next scheduled dose to avoid drug overdose. The drug is recommended for one dose twice weekly only. Consult the healthcare provider for better guidance about the dosage.
Drug Storage and Disposal:
The drug (tablets and oral suspensions) should be stored at a room temperature of 22 to 25 degrees Celsius, or 68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit. It should be stored in its original airtight container, and the oral suspension must not be frozen.
Keep the drug out of children’s reach. Unused or expired medication should not be stored, rather it should be discarded either through a take-back program by contacting the nearest pharmacist, or by following the drug disposal protocols given by FDA. The drug should not be flushed or thrown away randomly.
For Doctor:
What Is the Clinical Pharmacology of the Drug?
Mechanism of Action:
Brincidofovir is a pro-drug consisting of lipid molecules of conjugated Cidofovir, which mimics lysophosphatidylcholine, an endogenous lipid. This lipid allows the hijack of the endogenous lipid by causing the molecules to enter the infected cells. Further, this process causes the generation of Cidofovir by cleavage of lipid molecules. It leads to the formation of Cidofovir diphosphate, an active antiviral compound through phosphorylated.
The antiviral effects of the active antiviral compound are a result of two mechanisms. According to recombination vaccinia DNA (deoxyribonuclease) polymerase studies, the antiviral compound inhibits orthopoxvirus DNA polymerase-mediated DNA synthesis. Also, it is an acyclic nucleotide analogue of deoxycytidine monophosphate; therefore, it can be incorporated into the viral DNA chain (growing), to slow the synthesis rate of viral DNA.
Pharmacodynamics:
The time course of pharmacodynamics responses, and exposure-response relationships of Brincindofovir and its active metabolite, Cidofovir diphosphate is still not known.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption
The Oral bioavailability of the drug in suspension formulation and tablet formulation is 16.8 % and 13.4 % respectively. After oral administration of the drug; Cmax (maximum concentration) and AUCtau (area under the plasma concentration-time curve) are 480 ng/mL and 3400ng hr/mL. respectively. Cmax and AUCtau ( for active metabolite, Cidofovir diphosphate) 9.7 pg/106 and 1200 pg/106 cells respectively.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of the drug is 1230 L.
Metabolism
Being a pro-drug of Cidofovir, Brincidofovir undergoes basic metabolic reactions to become pharmacologically active. Therefore, the phosphodiester bond of the drug gets hydrolyzed to form Cidofovir, which further gets phosphorylated to form Cidofovir diphosphate, an active metabolite of the drug. The inactive metabolites of the drug are CMX064 and CMX103, which are generated by carboxylation, oxidative reactions, and fatty acid oxidation, mediated by CYP4F2.
Elimination
The drug gets eliminated from the body by approximately 51 percent in urine and about 40 percent in feces. The terminal half-life of the drug and its active metabolite is 19.3 hours, and 113 hours respectively.
Ingredients
Active Ingredient: Brincidofovir
Inactive Ingredient:
- Tablets - Crospovidone, colloidal silicon dioxide, mannitol, FD&C blue #1/brilliant blue FCF aluminum lake, magnesium stearate, FD&C blue #2/indigo carmine aluminum lake, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, purified water, polyethylene glycol, silicified microcrystalline cellulose, titanium dioxide, and talc.
- Oral Suspension - Lemon lime flavor, citric acid anhydrous, microcrystalline cellulose, purified water, carboxymethyl cellulose sodium, simethicone 30 percent emulsion, trisodium citrate anhydrous, sodium benzoate, xanthan gum, and sucralose.
Dose Form and Strength:
- Tablets: Brincidofovir tablets are oval-shaped, blue, film-coated debossed with BCV on one side and 100 on the other side. Each tablet has a strength of 100 mg Brincidofovir.
- Oral Suspension: It is white-to-off white opaque, aqueous bases, lemon-lime suspension, having a strength of 10 mg/mL of Brincidofovir.
Warnings and Precautions
Mortality Due to Prolonged Drug Usage: The drug is not to be used in any other condition except for smallpox. Also, prolonged use of drugs (more than the recommended dosage on Days one and eight), can increase the risk of mortality.
Diarrhea and Gastrointestinal Effects: The drug has been known to cause diarrhea and other gastrointestinal adverse events. Therefore, a person should be carefully monitored for dehydration and diarrhea, after prescribing the dosage, and in case of any such events, the second and final dose of the drug should be avoided. Supportive care should be given to a patient
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: As per animal reproduction studies, the drug can cause harm to the fetus, when administered to pregnant individuals. It has also caused embryotoxicity and structural malformations in rabbits and rats. Therefore, alternative therapy for the treatment of smallpox should be opted for by the doctor in a pregnant person.
Elevation in Bilirubin and Hepatic Transaminases: The drug can cause an elevation in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and total bilirubin. Therefore, a hepatic laboratory examination should be conducted before prescribing the drug to a patient. The drug is known to cause adverse events, such as acute hepatitis, hyperbilirubinemia, or hepatic steatosis.
Carcinogenicity: The drug has the potential to cause carcinogenic effects. The systematic exposure of the drug less than the recommended human drug exposure has been known to cause squamous cell carcinoma and mammary adenocarcinomas in rats. Therefore, the drug should not be divided or crushed, and direct contact with the drug after crushing the tablet and with the oral suspension should be avoided. The exposed skin area should be washed with water thoroughly.
Male Infertility: According to testicular toxicity studies on animal models, the drug has the potential to irreversibly cause infertility in males.
Co-administration with Similar Products: The drug should not be co-administered with Cidofovir, as being a derivative of lipid-linked Cidofovir, it can get coveted to Cidofovir.
What Are the Drug Interactions of Brincidofovir?
- Interactions With Other Drugs:
Concomitant use of Brincidofovir with other drugs, such as cyclosporins, Erythromycin, hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) protease inhibitors, Gemfibrozil, Clarithromycin, Rifampin, and other 1B3 or OATP1B1 inhibitors, increased Cmax and AUC and thus causes Brincidofovir-associated adverse effects.
- Vaccine Interactions:
Vaccine-drug interaction studies have not been performed on humans; however, the coadministration of Brincidofovir with live smallpox vaccine or vaccinia virus has been shown to reduce the immune response to the vaccine. The clinical impacts on the efficacy of the vaccine due to these potential interactions are also not known.
Patient Counseling Information:
-
The doctor should inform the patient that the drug’s efficacy is only based on animal studies, and its effectiveness is not yet studied on humans, before prescribing the drug.
-
The patient should also be informed about the liver testing before and during the treatment with Brincidofovir as it may cause symptoms of liver damage or injury. Also, they should be informed to report immediately if any such symptoms are experienced by them during the course of treatment.
-
The doctor must also inform the patient about gastrointestinal adverse events associated with Brincidofovir, such as dehydration and diarrhea, and that they should report this to the doctor immediately to avoid severe conditions.












